When it comes to tackling obesity, we have heard it all: cut carbs, eat more protein, count calories, and the list goes on.
But there is a relatively simple yet powerful concept that is gaining traction among nutritionists and health experts: nutrient density.
Could focusing on nutrient dense foods be the game-changer we have been searching for?
LeanAndFit shall explore how prioritizing nutrient-dense foods over calorie-dense ones might be the secret weapon against obesity.
Is Nutrient Density the Secret Weapon Against Obesity” Article Contents
- What is Nutrient Density?
- Nutrient Dense Foods vs. Calorie Dense Foods
- The Role of Nutrient Density in Obesity Management
- The Benefits of a Nutrient Dense Diet
- Choosing Nutrient Dense Vegetables and Proteins
- Strategies to Incorporate Nutrient Density into Your Diet
- FAQs on Nutrient Density and Obesity Treatment
- Conclusion: Is Nutrient Density the Answer?
What is Nutrient Density?
Nutrient density refers to the amount of essential nutrients a food provides relative to the number of calories it contains.
Essentially, nutrient-dense foods deliver a high level of vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds for a relatively low calorie count.
For example, a cup of spinach is packed with vitamins A, C, K, and iron but has only about 7 calories, making it a nutrient powerhouse.
In contrast, calorie dense foods are high in calories but often low in nutrients.
Think of sugary snacks, fast food, and processed items that may leave you feeling full but do not nourish your body.
Focusing on nutrient density means you get more nutritional bang for your buck, which can help support weight loss and overall health.
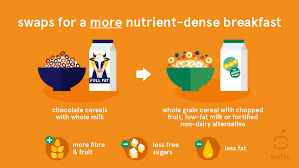
Nutrient Dense Foods vs. Calorie Dense Foods
Understanding the distinction between nutrient-dense and calorie-dense foods is key to managing weight effectively and sustainably. Nutrient-dense foods provide a high amount of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and beneficial compounds for relatively few calories. Calorie-dense foods, by contrast, pack a lot of energy—often from added sugars and unhealthy fats—into small portions, with minimal nutritional value.
Take, for example, a bowl of quinoa versus a serving of French fries. Both may offer similar calorie content, but quinoa delivers protein, iron, magnesium, and fiber, while fries mainly provide fat, starch, and sodium. This difference has major implications for satiety and metabolic health.
Nutrient-dense foods like leafy greens, berries, legumes, whole grains, and lean proteins help regulate hunger hormones, stabilize blood sugar levels, and prevent overeating.
Their fiber content slows digestion, promoting a feeling of fullness that lasts longer than that from ultra-processed foods. In contrast, calorie-dense options—such as pastries, chips, and sugary drinks—can lead to rapid spikes and crashes in blood glucose, triggering cravings and excessive caloric intake. So, it is wise to adopt calorie deficit in your diet pattern.
According to the CDC, people who consume more nutrient-dense foods tend to have healthier body weights and a lower risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Incorporating nutrient-dense options doesn’t mean sacrificing taste or satisfaction—it means choosing foods that work for your body rather than against it.
Ultimately, shifting from calorie-rich but nutrient-poor foods to nutrient-dense choices is a cornerstone strategy in obesity prevention and long-term weight management.
The Role of Nutrient Density in Obesity Management
Incorporating nutrient-dense foods into your diet can play a significant role in managing obesity.
Studies have shown that a diet high in nutrient density in food can lead to better health outcomes, including weight loss and reduced risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease such as arterial stiffness.
Unlike fad diets that focus solely on calorie restriction, a nutrient dense diet ensures that your body receives the essential nutrients it needs to function properly.
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition found that diets rich in nutrient-dense foods are associated with lower body weight and better metabolic health.
By focusing on quality over quantity, you’re more likely to sustain weight loss and avoid the pitfalls of typical restrictive diets.
The Benefits of a Nutrient Dense Diet
Well, here is how watching out for nutrients helps you:
-
Improved Satiety
Nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are high in fiber and water content. Fiber slows digestion and promotes a feeling of fullness, signaling your brain that you have had enough to eat. This reduces the temptation to overeat or snack unnecessarily, making weight loss more sustainable over time. -
Reduced Cravings
When you consume balanced meals rich in nutrients, your blood sugar levels remain more stable. This prevents the glucose spikes and crashes that typically trigger cravings for processed, calorie-dense snacks. By avoiding these highs and lows, you are less likely to reach for sugary or fatty “comfort” foods. -
Enhanced Metabolic Health
A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber helps optimize metabolic function. It improves insulin sensitivity, reduces triglycerides, and balances cholesterol levels. These changes support better glucose control and lower the risk of obesity-related metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease. -
Prevention of Nutrient Deficiencies
Nutrient-dense eating ensures you get essential micronutrients like magnesium, vitamin D, iron, and B-vitamins. These are crucial for energy production, immune function, and mood regulation. Deficiencies in these nutrients can lead to fatigue, brain fog, poor recovery, and weakened resilience to stress—all of which indirectly sabotage healthy lifestyle efforts. -
Long-Term Health Benefits
Over time, prioritizing nutrient-dense foods can help lower inflammation, support gut health, and reduce the risk of chronic illnesses such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoporosis—making this dietary approach both practical and preventive.
Choosing Nutrient-Dense Foods for a Healthier Diet
A nutrient-dense diet focuses on selecting foods that provide the highest amount of essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients with minimal calories. Incorporating these foods can improve overall health, support weight management, and boost energy levels.
Here are some of the best options:
1. Leafy Green Vegetables:
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as minerals like iron and calcium. These nutrients are essential for bone health, immune function, and reducing inflammation. According to Eating Well, a cup of cooked spinach provides high amounts of these nutrients while being low in calories, making it an excellent addition to any diet.
2. Lean Proteins:
Protein plays a crucial role in muscle development and metabolism. Sources like chicken breast, turkey, and fish are high in protein but low in unhealthy fats. The American Heart Association emphasizes the importance of consuming lean proteins to promote heart health and maintain muscle mass.
3. Legumes and Beans:
Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are packed with plant-based protein and dietary fiber, which aid digestion and promote satiety. Chickpeas, for example, contain essential nutrients like folate, iron, and phosphorus. According to Wikipedia, they are one of the most nutrient-dense legumes available.
4. Fatty Fish:
Salmon, sardines, and mackerel are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which support brain and heart health. Healthline states that fatty fish provide high-quality protein and essential nutrients, making them a key component of a nutrient-rich diet.
5. Nuts and Seeds:
Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are packed with healthy fats, protein, and fiber. They also contain essential minerals like magnesium and zinc. Mount Sinai Medical Center highlights that flaxseeds are one of the richest sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid linked to reduced inflammation.
6. Berries:
Blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber, helping to support immune function and lower the risk of chronic diseases. According to Real Simple, berries are among the most nutrient-dense fruits due to their high concentration of polyphenols and vitamins.
7. Whole Grains:
Quinoa, brown rice, and oats provide sustained energy and are excellent sources of fiber, B vitamins, and essential minerals. The American Heart Association recommends incorporating whole grains into daily meals to support heart health and digestion.
By prioritizing these nutrient-dense foods, individuals can create a balanced diet that supports long-term health and well-being while maintaining a healthy weight.
Strategies to Incorporate Nutrient Density into Your Diet
- Swap Out Calorie Dense Foods: Replace high-calorie, low-nutrient foods like chips and sugary cereals with nutrient-rich alternatives like nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Choose Low Calorie High Density Foods: Foods like berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables are not only packed with nutrients but also low in calories, making them perfect for weight management.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods over packaged options. Whole foods naturally have a higher nutrient density compared to their processed counterparts.
- Balance Your Plate: Aim to fill half your plate with vegetables, a quarter with lean protein, and a quarter with whole grains or legumes. This ensures a balanced intake of macronutrients and micronutrients.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues. Eating slowly and mindfully can help you better appreciate nutrient-dense foods and prevent overeating.
FAQs on Nutrient Density and Obesity Treatment
Q-1: If calories drive weight, why does nutrient density matter at all?
A-1: Because how you reach a calorie target shapes hunger and adherence. Foods rich in protein, fiber, water, and micronutrients deliver more fullness per calorie, so you naturally stop sooner without white-knuckle restraint. Think salmon + beans + leafy greens vs. pastries: same calories on paper, but the nutrient-dense plate produces slower gastric emptying, steadier glucose, and less snack-seeking two hours later.
Q-2: Can micronutrient gaps really make me overeat?
A-2: Often indirectly. When meals are low in key nutrients (protein, potassium, magnesium, iron), your brain receives a weaker “nutritional satisfaction” signal. You keep chasing more food to fill the gap—usually from convenient, energy-dense options. Closing those gaps with nutrient-dense choices (legumes, greens, seafood, dairy/yogurt, nuts, eggs) reduces that background drive and makes a modest calorie deficit feel easier.
Q-3: What simple metric helps me spot nutrient-dense meals quickly?
A-3: Use a protein-to-energy check: aim for ~25–40 g protein per main meal while keeping added sugars and refined fats modest. Then add fiber per calorie—about 10–15 g fiber per 1,000 kcal. A bowl that hits both (e.g., Greek yogurt + oats + berries + walnuts) tends to satisfy more on fewer calories than a low-protein, low-fiber equivalent.
Q-4: Are smoothies and “healthy” bars as nutrient-dense as whole foods?
A-4: Not usually in terms of satiety. Blending can reduce chewing and speed intake, while bars often pack concentrated fats/sugars with added isolates. Whole-food versions—an apple with peanut butter, or a lentil-veg bowl—deliver similar nutrients with more volume and viscosity, stretching time-to-fullness and curbing the urge for seconds.
Q-5: How do I build a nutrient-dense day that still fits real life?
A-5: Think anchor foods and assembly.
-
Breakfast: eggs or skyr + fruit + high-fiber cereal.
-
Lunch: bean-based soup + whole-grain wrap + salad.
-
Dinner: lean protein (fish/chicken/tofu) + two veg (one leafy, one colorful) + whole grain or potato.
-
Snacks: berries, edamame, kefir, nuts (pre-portioned).
Batch-cook proteins and grains on weekends, keep frozen veg for speed, and pre-portion nuts/dressings. You’ll hit nutrients first—calories fall in line.
Is Nutrient Density the Answer?
So, is nutrient density the secret weapon against obesity?
The answer is a resounding yes—when combined with other healthy lifestyle practices.
y focusing on nutrient dense foods, you can support weight loss and improve overall health without feeling deprived.
Unlike restrictive diets that often fail, a nutrient-dense approach is sustainable and promotes long-term health benefits.
While nutrient density alone isn’t a cure-all, it is a powerful tool in the fight against obesity.
Alongside regular physical activity and other obesity therapies, it provides a comprehensive, balanced approach to managing weight and improving well-being.
So, next time you plan your meals, think nutrient density—your body will thank you!
References:
