Ever wonder why some people can eat just about anything and never seem to gain weight, while others struggle with the scale despite their best efforts?
The answer could lie in something deeper than diet and exercise—our genes.
Specifically, leptin resistance is emerging as a major factor that may explain the genetic predisposition to obesity.
In this article, leanandfit.info will dive into what leptin resistance is, how it relates to obesity, and whether it could be the hidden genetic trigger behind your weight gain struggles.
We will explore the scientific evidence on leptin resistance, discuss the role of leptin levels in obesity, and even touch on medical interventions like Saxenda for managing leptin resistance.
Article Index
- What is Leptin?
- The Role of Leptin in Obesity
- How Does Leptin Resistance Develop?
- The Genetic Link: Leptin Resistance and Obesity
- Leptin Resistance and Weight Gain
- Medical Interventions: Saxenda and Leptin Resistance
- The Impact of Low Leptin Levels on Obesity
- FAQs on Leptin Resistance and Obesity
- Can Leptin Resistance Be Reversed?
- Conclusion: Is Leptin Resistance Really the Genetic Trigger for Obesity?
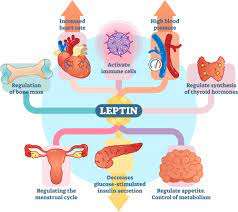
What is Leptin?
Leptin is a hormone produced primarily by your body’s fat cells. Often referred to as the “satiety hormone” or “fat hormone,” leptin plays a crucial role in regulating your appetite and energy balance.
When leptin levels are high, it signals to your brain that you’re full, reducing the urge to eat.
However, when leptin levels are low, your brain is signaled to eat more, leading to weight gain if the cycle is not well-regulated.
The Role of Leptin in Obesity
For most people, leptin—the so-called “satiety hormone”—works like a charm, signaling the brain when it’s time to stop eating.
But sometimes, this finely tuned system goes haywire.
Enter leptin resistance. In this scenario, your body keeps churning out leptin, but your brain misses the memo.
It is like your “full tank” light is broken, so you keep refueling unnecessarily.
The result?
You feel constantly hungry, keep eating, and your body stores even more fat, which only cranks up leptin levels further—a vicious cycle that’s tough to break.
Over time, this leads to persistent weight gain and increased fat storage.
A study published in Nature Reviews Endocrinology confirms that leptin resistance is strongly linked to obesity, especially in those with a genetic predisposition.
Think of it as your body’s hunger thermostat malfunctioning—it is not your willpower failing, but a metabolic mix-up.
Addressing leptin resistance is key to breaking the overeating cycle and restoring balance. This is similar to inherited metabolism towards obesity but has its own uniqueness.
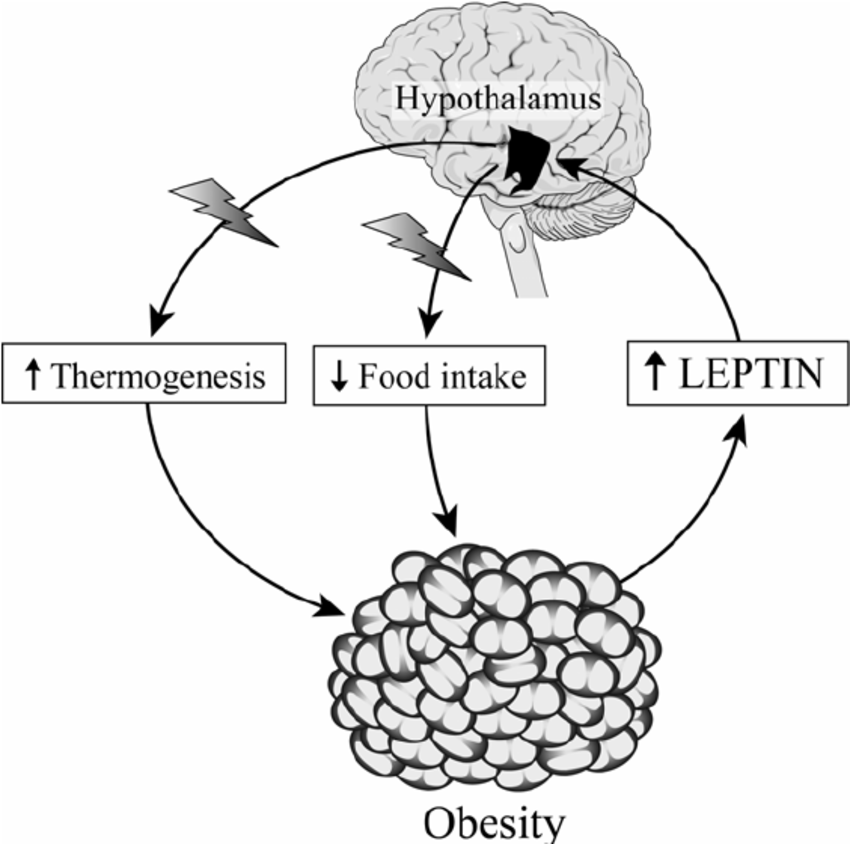
How Does Leptin Resistance Develop?
Leptin resistance can develop for several reasons, with prolonged high leptin levels due to excessive fat storage being one of the primary culprits.
When leptin levels remain elevated for extended periods, the brain gradually becomes less responsive to the hormone’s signals.
This results in the need for ever-increasing leptin levels to achieve the same satiety effect, creating a feedback loop that contributes to overeating and further fat accumulation.
Obesity and chronic inflammation are closely linked to leptin resistance. High-fat diets and chronic overeating exacerbate the problem by promoting inflammatory responses that impair leptin signaling.
According to research published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, inflammation disrupts leptin’s ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, further limiting its effectiveness.
Genetics also play a significant role in leptin resistance.
Studies suggest that certain genetic mutations, particularly in the LEPR gene, predispose individuals to develop leptin resistance and obesity more easily than others, highlighting the complex interaction between genes and metabolism.
The Genetic Link: Leptin Resistance and Obesity
Leptin resistance and obesity have a well-documented genetic link.
Research published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation shows that individuals with certain genetic mutations are more likely to have defective leptin signaling pathways, which contribute to a higher risk of developing obesity.
These genetic predispositions can cause leptin resistance in obesity by interfering with the body’s ability to regulate hunger and energy expenditure.
Essentially, when leptin can’t signal the brain properly due to these mutations, the body struggles to manage weight, leading to significant fat storage.
Leptin Resistance and Weight Gain
How exactly does leptin resistance lead to weight gain?
It is like your body’s hunger switch is stuck in the “on” position.
Leptin’s job is to signal your brain when you’ve had enough to eat. But in leptin resistance, this signal never gets through, leaving the body in a state of constant hunger and driving overeating.
With the brain unable to recognize satiety, you’re more likely to consume excess calories, which are stored as fat. Over time, this creates a cycle of persistent weight gain.
Imagine someone diligently following a strict diet and exercise plan but still struggling to lose weight.
Despite their efforts, their body’s leptin signaling is impaired, making it harder to shed fat because their brain still thinks they’re starving.
This is not a matter of willpower—it is a biological roadblock.
Scientific studies, such as one published in The Journal of Endocrinology, show that leptin resistance is closely linked to obesity and metabolic syndrome, particularly in individuals with chronic inflammation or a high-fat diet.
This condition rewires the body to store fat rather than burn it, making sustainable weight loss a significant challenge.
Medical Interventions: Saxenda and Leptin Resistance
Saxenda (liraglutide), an FDA-approved medication for obesity, is showing promise not only in weight loss but also in potentially improving leptin resistance.
While Saxenda primarily mimics glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and suppresses appetite, its benefits may extend beyond these functions.
Emerging research indicates that Saxenda may enhance leptin sensitivity, particularly in individuals struggling with obesity-related leptin resistance.
A study published in Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism found that patients using Saxenda experienced reductions in leptin levels proportional to their weight loss, which could reset leptin signaling pathways.
This suggests that Saxenda may indirectly reduce leptin resistance by promoting fat loss and lowering chronic inflammation—two key contributors to leptin dysfunction.
In some patients, this improved sensitivity helped restore the brain’s response to leptin, making it easier to maintain weight loss over time.
Although further research is needed to confirm its long-term effects on leptin signaling, Saxenda represents a promising option for individuals struggling with leptin resistance and related weight gain, offering a new approach to addressing this complex metabolic challenge.
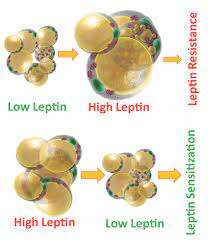
The Impact of Low Leptin Levels on Obesity
Interestingly, some individuals have low leptin levels despite having excess body fat, a rare condition that highlights how complex leptin’s role in body weight regulation really is.
Typically, leptin levels rise with increased fat stores, signaling the brain to reduce appetite. Leptin resistance stops weight loss dead in its tracks.
However, in cases of congenital leptin deficiency or rare genetic mutations, leptin production is abnormally low, leaving the brain with no signal to curb hunger.
As a result, these individuals continue to overeat, leading to severe obesity, despite having substantial fat reserves.
This situation creates a paradox: the body stores fat yet behaves as though it is in a state of starvation, driving persistent hunger and rapid weight gain.
For example, a patient with congenital leptin deficiency may feel uncontrollable hunger soon after eating a large meal because their brain never receives the “full” signal.
Scientific studies, including one published in The New England Journal of Medicine, confirm that leptin replacement therapy in such patients can restore normal hunger signals and lead to substantial weight loss.
These findings reinforce that leptin signaling, rather than just leptin levels, plays a vital role in managing body weight and appetite control.
Understanding these mechanisms may open doors to new treatments for obesity beyond calorie restriction and exercise.

FAQs on Leptin Resistance and Obesity
Can Leptin Resistance Be Reversed?
The good news is that leptin resistance can be managed, though reversing it entirely is challenging.
Weight loss, especially through dietary changes and increased physical activity, has been shown to improve leptin sensitivity.
Losing just 5–10% of body weight can significantly lower leptin levels, helping the brain recognize satiety signals again.
Inflammation, a key factor in leptin resistance, can also be reduced by adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in whole foods, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants.
Regular physical activity, particularly strength training and aerobic exercise, further reduces inflammation and improves metabolic health.
A study published in the Journal of Obesity found that combining reduced calorie intake with regular exercise led to notable improvements in leptin sensitivity among obese individuals.
However, since leptin resistance is linked to genetic predisposition in some cases, long-term lifestyle changes are often necessary to maintain these improvements.
While there is no quick fix, consistent healthy habits can help restore leptin function, improve appetite control, and reduce the risk of obesity-related complications.
Is Leptin Resistance Really the Genetic Trigger for Obesity?
So, is leptin resistance the hidden genetic trigger for obesity?
The answer is a resounding yes—but it is not the only factor.
While leptin resistance is undoubtedly linked to genetic predisposition and plays a crucial role in obesity, environmental factors such as diet, physical activity, and lifestyle habits also contribute.
For those struggling with weight gain due to leptin resistance and obesity, a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions like Saxenda can provide a comprehensive solution.
Ultimately, managing leptin resistance involves addressing both genetic and environmental factors to achieve lasting weight loss.
References: