Obesity is a growing health concern across the globe, but many people are unaware of how it directly impacts their respiratory system.
Airway obstruction, in particular, is a severe consequence of obesity, making it difficult for individuals to breathe properly, especially during sleep or physical exertion.
In this article, leanandfit.info will explore how excess body fat can cause airway obstruction, backed by scientific studies and evidence.
You will learn how this condition develops, its dangerous effects, and how addressing obesity can relieve the airway obstruction.
Article Contents:
- Introduction to Obesity and Airway Obstruction
- The Mechanics of Airway Obstruction in Obesity
- Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS)
- Sleep Apnea and Airway Obstruction
- How Fat Deposits in the Neck Worsen Airflow
- Increased Risk of Respiratory Infections
- Lung Function Decline in Obese Individuals
- The Role of Inflammation in Airway Obstruction
- FAQs on Obesity and Breathing Issues
- Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Airway Obstruction
- Conclusion: Does Obesity Cause Dangerous Airway Obstruction?
Introduction to Obesity and Airway Obstruction
Airway obstruction occurs when the airway becomes blocked or narrowed, restricting airflow to the lungs. This can be partial or complete and significantly impacts breathing, especially during sleep.
One major contributor to airway obstruction is obesity, which is closely linked to upper airway narrowing, particularly in the throat and neck regions. Excess fat deposits around the neck can compress the airway, increasing the likelihood of breathing difficulties.
When the airway is narrowed, the body struggles to maintain adequate airflow, especially when lying down. This often leads to conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS).
OSA causes breathing to stop and start repeatedly during sleep, leading to poor oxygenation and fragmented rest. It is associated with serious health risks such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
OHS, on the other hand, is a more severe condition where excessive body weight affects the respiratory system’s ability to maintain normal oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, causing chronic breathing problems.
Addressing obesity and improving airway function is crucial for reducing these risks and improving overall health.
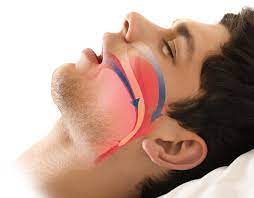
The Mechanics of Airway Obstruction in Obesity
In obese individuals, excess fat does not just accumulate around vital organs—it also builds up in the neck and chest, creating unexpected breathing challenges.
Fat deposits in the neck can narrow the airway, making it harder for air to pass through, especially during sleep or physical activity. This narrowing often causes airway obstruction, which can feel like a “choking” sensation or shortness of breath.
When airflow is restricted, the body struggles to get enough oxygen, putting extra stress on the heart and lungs.
Over time, this oxygen shortage takes a toll on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of serious conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and even stroke.
It’s not just about feeling out of breath—it’s a signal that your body needs attention. Addressing obesity can help reduce these risks, improve breathing, and lead to better overall health and well-being.
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS)
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS) is a serious condition in which severely obese individuals fail to breathe deeply or adequately, resulting in reduced oxygen levels and a dangerous buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood (hypercapnia).
This occurs because excess fat in the chest wall, abdomen, and neck area compresses the respiratory system, making it harder for the lungs to expand fully. This restricted breathing pattern forces the body to work harder to get enough air, eventually exhausting the respiratory muscles.
According to clinical research, approximately 90% of individuals with OHS also suffer from obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), further compounding the problem.
Sleep apnea causes frequent pauses in breathing during sleep, which worsens oxygen deprivation and disrupts restorative rest.
If left untreated, OHS can be life-threatening. It increases the risk of chronic fatigue, high blood pressure, heart failure, and pulmonary hypertension—conditions that can significantly reduce life expectancy.
A study published in Chest Journal found that untreated OHS increases mortality risk compared to obesity alone. Early diagnosis and treatment, including weight management, non-invasive ventilation (CPAP or BiPAP), and lifestyle changes, are crucial for improving outcomes.
Sleep Apnea and Airway Obstruction
One of the most common and serious complications of obesity is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a condition where the airway becomes blocked during sleep, causing breathing to repeatedly stop and start throughout the night.
This blockage often results from excess fat around the neck and throat, narrowing the airway and restricting airflow.
According to the American Thoracic Society, nearly 70% of obese individuals experience sleep apnea, making it a widespread but underdiagnosed condition.
Each time breathing stops, the brain briefly wakes the body to restart the airflow. These micro-awakenings often go unnoticed but disrupt sleep cycles, preventing deep, restorative sleep.
Over time, this leads to chronic fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and irritability. Even more concerning, untreated sleep apnea significantly increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
Addressing OSA through weight loss, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, and lifestyle changes can dramatically improve sleep quality and overall health.
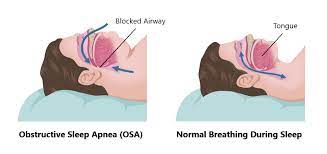
How Fat Deposits in the Neck Worsen Airflow?
Excess fat in the neck region isn’t just an accessory you don’t need—it is a troublemaker when it comes to breathing. These fat deposits don’t sit quietly; instead, they press on the upper airway tissues, narrowing the space where air should flow freely.
This added pressure increases the risk of airway collapse during sleep, making every breath a struggle. It’s like having a pillow fight with your own throat—and losing.
What’s more, studies have shown that neck circumference is one of the strongest predictors of sleep apnea severity. Think of it this way: the thicker the neck, the greater the chance that your airway might pull a disappearing act at night.
So, if your neck is measuring on the generous side, it might be time to pay attention. Reducing body fat can help reclaim your airway, improve sleep quality, and make breathing the breeze it’s supposed to be.
Research from the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine found that individuals with a neck circumference greater than 17 inches are at a higher risk of airway obstruction during sleep.
Increased Risk of Respiratory Infections
Obesity significantly elevates the risk of respiratory infections, further exacerbating airway obstruction.
Excess adipose tissue contributes to a chronic, low-grade inflammatory state, impairing both innate and adaptive immune responses. This immune dysfunction weakens the body’s defenses against pathogens, increasing susceptibility to infections.
Research indicates that obesity is associated with an increased risk of severe respiratory infections, including influenza and COVID-19.
Moreover, the mechanical impact of excess weight on the respiratory system leads to reduced lung volumes and airway narrowing, creating an environment conducive to infections like chronic bronchitis.
This condition involves persistent inflammation of the bronchial tubes, resulting in mucus buildup and further airway obstruction.
The combination of impaired immune function and mechanical respiratory limitations in obese individuals underscores the importance of weight management and proactive respiratory care to mitigate infection risks and maintain airway health.
Lung Function Decline in Obese Individuals
Obesity has a profound impact on lung function, leading to a noticeable reduction in lung volume and capacity.
Excess fat around the chest and abdomen compresses the lungs, making it difficult for them to expand fully with each breath.
Studies show that obese individuals often experience a decline in lung capacity, which can result in shallow breathing and decreased oxygen intake.
One common consequence is restrictive lung disease, a condition in which the lungs’ ability to expand is limited, reducing the amount of oxygen they can absorb.
This restriction worsens airway obstruction and can cause shortness of breath during even mild physical activities.
According to a study published in the European Respiratory Journal, lung function progressively declines as body mass index (BMI) increases. This means the higher the BMI, the greater the respiratory burden.
Addressing obesity through weight loss and physical activity can significantly improve lung function and reduce respiratory complications.
The Role of Inflammation in Airway Obstruction
Chronic inflammation plays a major role in how obesity contributes to airway obstruction and respiratory issues.
Excess body fat, particularly in the abdominal and neck regions, is not just stored energy—it’s biologically active and produces inflammatory molecules called cytokines.
These cytokines promote inflammation throughout the body, including the airways, causing swelling and narrowing that restricts airflow.
Over time, this persistent inflammation can significantly affect lung health, increasing susceptibility to respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
A study published in the Journal of Inflammation found that obese individuals exhibit higher levels of airway inflammation compared to those with a healthy weight, making breathing more difficult.
This airway inflammation, when left unchecked, worsens airway obstruction and reduces lung function, further complicating respiratory health.
Reducing inflammation through weight loss, physical activity, and an anti-inflammatory diet can help restore airway health and improve overall breathing capacity.
FAQs on Obesity and Breathing Issues
Q-1: Why does a larger waistline make my throat collapse at night?
A-1: Extra fat does not just sit under the skin—it can infiltrate the tongue and the soft tissues around the pharynx, narrowing the airway. At the same time, abdominal fat reduces lung volumes (especially functional residual capacity), which normally “tethers” the airway open. With less caudal traction and a thicker, softer throat, the tube collapses more easily during sleep, especially in supine positions.
Q-2: What makes neck size such a strong predictor of snoring and sleep apnea?
A-2: Neck circumference is a quick proxy for how much soft tissue surrounds the upper airway. More tissue means higher external pressure on the pharyngeal walls and more mass in the tongue base. Add fluid shifting toward the neck when you lie down, and the airway’s critical closing pressure rises. That is why even modest evening salt/alcohol can tip a “borderline” airway into loud snoring or obstructive events.
Q-3: Can obesity obstruct breathing even when I’m awake and sitting?
A-3: Yes. Central fat loads the chest wall, increasing the effort needed for each breath. Smaller end-expiratory lung volumes amplify airway resistance, and low-grade systemic inflammation can thicken and hyperreact small airways. The result is a “double hit”: mechanically harder breathing and more collapsible peripheral airways—felt as breathlessness climbing stairs or tightness during mild colds.
Q-4: Why are anesthesia, sedatives, and opioids riskier for people with obesity?
A-4: Sedatives relax the muscles that stiffen the airway; opioids blunt the brain’s drive to breathe. In obesity, the baseline airway is narrower and more collapsible, so a routine dose can precipitate obstruction or hypoventilation. Supine positioning further reduces lung volumes. Safer practice includes ramped positioning (head and shoulders elevated), careful dosing, continuous oximetry/capnography, and early use of CPAP/NIV when indicated.
Q-5: What immediate changes reduce obstruction risk while longer-term weight loss is in progress?
A-5: Sleep on your side or with the head of the bed elevated; avoid alcohol within 3–4 hours of bedtime; use nasal decongestion or mandibular advancement devices if recommended; and keep evening fluid/salt modest to limit rostral fluid shifts. Aim for gradual weight loss, consistent aerobic activity, and resistance training to raise lung volumes and strengthen upper-airway dilators. If daytime sleepiness, witnessed apneas, or morning headaches occur, seek formal evaluation—untreated obstruction raises blood pressure, arrhythmia, and accident risk.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Airway Obstruction
The good news is that lifestyle changes can greatly reduce the risk of airway obstruction in obese individuals.
Even modest weight loss—just 5-10% of body weight—can lead to significant improvements in airway patency (the openness of the airway) and reduce the severity of conditions like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Studies have shown that as body weight decreases, fat deposits around the neck and chest diminish, relieving pressure on the upper airway and improving breathing during sleep and physical activity.
Weight loss strategies such as regular exercise and healthy dietary changes are key components in managing airway obstruction. Cardiovascular activities, in particular, help improve lung capacity and oxygen intake.
For individuals struggling with severe obesity, bariatric surgery is an effective option that not only promotes rapid weight loss but also improves respiratory function and overall health.
By addressing the root cause—excess body weight—these lifestyle modifications can restore proper airway function and enhance quality of life.
Takeaway
In conclusion, obesity is a major contributing factor to dangerous airway obstruction.
Excess fat in the neck and chest compresses the airway, leading to conditions such as sleep apnea, obesity hypoventilation syndrome, and an increased risk of respiratory infections.
Furthermore, lung function decline and chronic inflammation caused by obesity exacerbate the problem, making it difficult for individuals to breathe properly.
Addressing obesity through lifestyle changes, weight loss, and medical interventions can significantly reduce airway obstruction and improve overall respiratory health.
References: